How to Identify and Correct Heading Indicator Errors: A Pilot’s Guide
Oct 02, 2024
Unlock the secrets to safer skies with our comprehensive guide on identifying and correcting heading indicator errors. Pilots, enhance your navigational skills with these practical insights empowering you to fly with precision and confidence.
Discover how mastering this vital aspect can elevate your aviation expertise and ensure smooth, error-free flights. Read on for key strategies!
Key Role of the Heading Indicator
The heading indicator is a primary flight instrument that allows you to determine the aircraft's direction from magnetic north, making it a key part of safe navigation. Its main job is to give you the heading information you need for controlled flight paths.
Alternative Names and Significance
Also known as Directional Gyro (DG) or Directional Indicator (DI) it’s all about precision in aviation. The other names tell you it’s all about keeping the aircraft oriented and directionally stable throughout the flight.
Instrument's Importance in Navigation
For the pilot the heading indicator provides information that informs navigation decisions and corrections. This helps safe flying and staying on track, that’s why it’s a critical navigation aid.
Helping Pilot Decision Making
By giving the pilot real-time data of the aircraft's heading, the heading indicator helps in decision-making. It allows the pilot to anticipate and make course corrections efficiently, overall safety and mission success.
Promoting Safety in Flight
In overall the heading indicator is the backbone of all navigation instruments, safety and reliability from takeoff to landing. The readings are crucial for confident flying, so pilots can navigate any airspace with clarity.
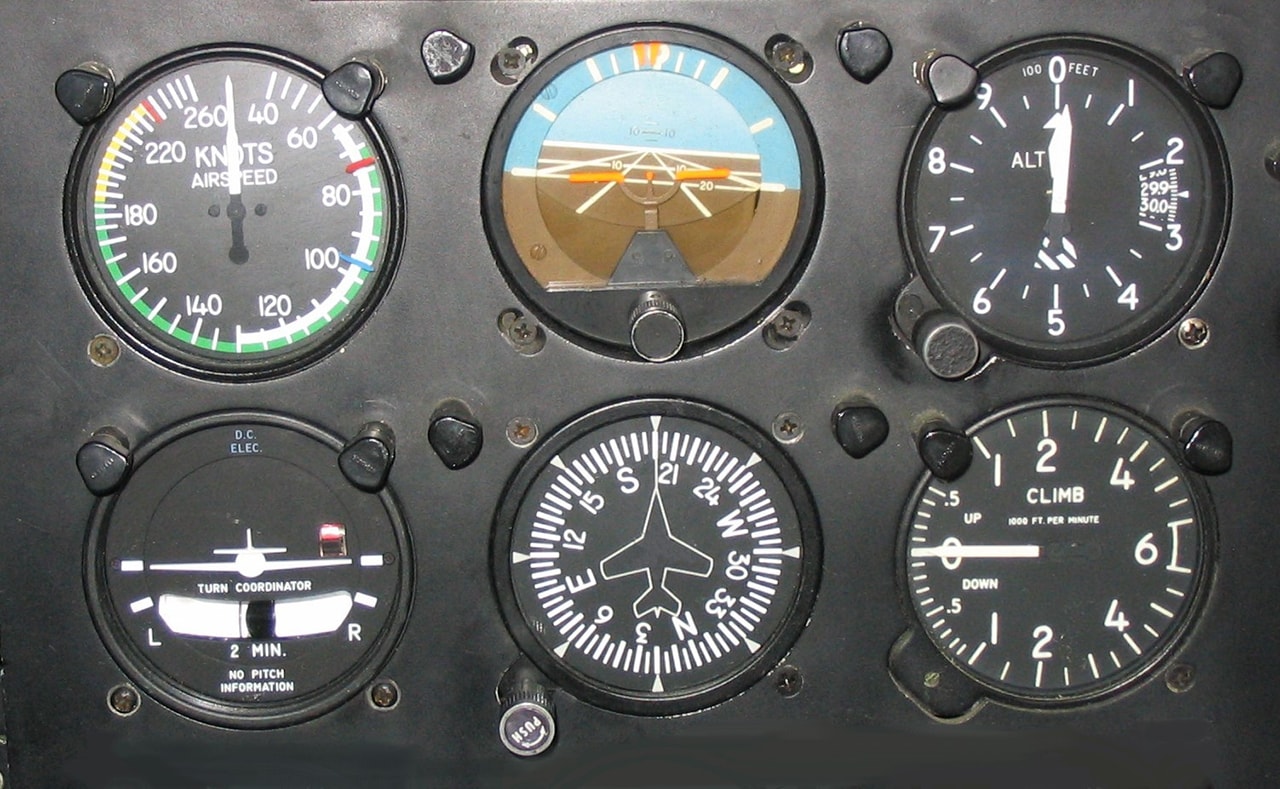

How the Heading Indicator Works
A Vital Instrument in Aviation
The heading indicator is key to precise navigation in aviation. It provides essential information about the aircraft's orientation, which is vital for understanding how does a heading indicator work.
By giving accurate readings, it helps keep your aircraft on course, stable, and directed throughout the flight.
Guiding Pilots Safely
Providing critical information, the heading indicator displays the direction that the aircraft's nose is pointed in relation to magnetic north, aiding navigational decisions by giving real-time input on the aircraft’s heading. This data is essential for pilots when making adjustments and ensuring that the flight path remains safe and controlled.
Supporting Informed Decisions
With constant updates on the aircraft’s heading, the heading indicator empowers pilots with the knowledge needed for informed and swift decision-making. This reliability helps pilots ensure the successful execution of their flight missions while enhancing flight safety.
Ensuring Safe Flight Operations
The heading indicator's role in aviation cannot be understated as it ensures pilots can navigate with confidence across different airspaces. This tool is fundamental in supporting safe and reliable flight journeys from departure to landing.

Understanding the Heading Indicator
Operating through a gyroscope, the heading indicator work involves measuring the rotational movement of the aircraft around its axis. By doing so, it provides pilots with precise directional information, crucial for maintaining the desired flight path during any maneuver.
Supporting Informed Decisions
With constant updates on the aircraft’s heading, the heading indicator empowers pilots with the knowledge needed for informed and swift decision-making. This reliability helps pilots ensure the successful execution of their flight missions while enhancing flight safety.
Ensuring Safe Flight Operations
The heading indicator's role in aviation cannot be understated as it ensures pilots can navigate with confidence across different airspaces. This tool is fundamental in supporting safe and reliable flight journeys from departure to landing.
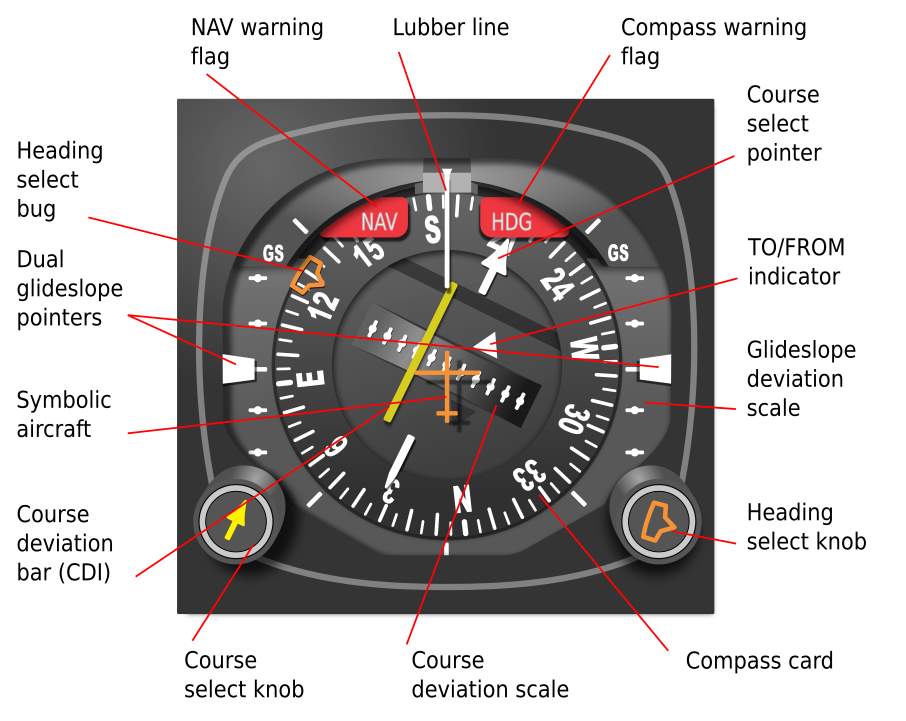
Key Differences: Heading Indicator vs. Magnetic Compass
Legacy of the Magnetic Compass and Heading Indicators
The magnetic compass (based on magnetic heading) has been around for ages in aviation and was the primary instrument for determining and setting an aircraft’s heading. Simple and based on the earth's magnetic field, it’s been a reliable tool for decades and has guided many a successful flight.
Similar Functions
Both the heading indicator and magnetic compass share the core function of providing the aircraft's heading. This information is vital for pilots to maintain their intended flight path, ensuring that they can navigate confidently through various airspaces.
Differences in Data Sources
The main difference between these two instruments is their data source. The magnetic compass uses the Earth’s magnetic field and the heading indicator uses a gyroscope. This difference in source affects how each instrument performs in different conditions.
Enhanced Precision
Using a gyroscope in the heading indicator is more precise than the traditional compass especially in areas of magnetic interference. By using this technology, pilots can make informed and accurate decisions and fly safer and more efficiently.
Common Errors and Causes
Mechanical drift is caused by friction in the gimbal of the heading indicator. This tiny bit of friction adds up over time and shows up as errors in the heading info on the instrument.
Apparent drift is caused by the Earth spinning. As pilots use ground references for navigation, the 15 degrees per hour the Earth rotates causes those references to move and affect heading accuracy.
Human error can also cause heading indication errors. If you don’t reset the heading indicator to the aircraft’s magnetic heading regularly, errors will creep in.
Vacuum pump failure is another thing that can affect the heading indicator. Since the heading indicator is vacuum pump dependent, if it fails the instrument will be inoperative.
Knowing these common mistakes and their causes is key to navigation and flight safety.
Be aware and check in time.

Types of Heading Indicator Errors
Heading indicators, like any other instrument, are prone to errors. Understanding these errors is crucial for pilots to ensure accurate navigation and safe flight. There are several types of heading indicator errors, including mechanical drift, apparent drift (precession), and other errors.
Mechanical Drift
Mechanical drift occurs due to the accumulation of friction within the heading indicator’s gimbal components.
This type of error is more common in older heading indicators, where worn bearings can increase the amount of friction-created drift.
Mechanical drift can cause the heading indicator to wander, leading to inaccurate readings. Regular maintenance and calibration can help minimize mechanical drift, ensuring that your heading indicator provides reliable information.
Apparent Drift (Precession)
Apparent drift, also known as precession, occurs due to the rotation of the Earth. The closer you are to the North or South Pole, the greater the hourly apparent drift.
At the equator, apparent drift is 0° per hour, while at the North Pole, it is 15° per hour.
This drift can accumulate over time, making it essential for pilots to correct for it regularly. By understanding and compensating for apparent drift, you can maintain accurate navigation throughout your flight.
Other Errors
Other errors that can affect heading indicators include human error, vacuum pump failure, and suction errors. Human error can occur if the pilot forgets to check gyro power and reset the heading indicator before take-off.
Vacuum pump failure can render the heading indicator inoperative, while suction errors can occur when the air flow over the gyro wheel is blocked or reduced.
Pilots must be aware of these potential errors and take corrective action to ensure accurate navigation. Regular checks and maintenance are key to preventing these issues and ensuring the reliability of your heading indicator.
Heading Indicator Errors Troubleshooting
Heading indicator errors troubleshooting starts with identifying the type of error. Knowing if it’s mechanical, apparent or human error will point you in the right direction. This is key to solving it efficiently.
Once you know the type of error, check the vacuum pump. A working vacuum pump is required for the heading indicator to work properly. Make sure it’s working and you’ll have accurate readings and confidence in your instrument.
Another step to troubleshoot is to reset the heading indicator. Align it with the aircraft’s magnetic heading and the instrument will show accurate information.
This will prevent many navigation errors during flight. If these don’t solve the problem, use other methods.
Instruments like the magnetic compass can be a reliable heading reference. By using multiple navigation tools pilots gain situational awareness and accuracy.
By doing these steps pilots can fix heading indicator errors. This proactive approach ensures safer flights and greater peace of mind, empowering pilots to navigate their journeys with precision and assurance.

Alignment and Calibration Procedures
Alignment and calibration is important for your heading indicator to give you accurate navigation information. Advanced flux gate systems make this easy with gyros that self align to the earths magnetic field, so you don’t have to lift a finger.
But if you’re flying with traditional heading indicators, then you’ll need to do it manually.
This means resetting the heading indicator to match the magnetic compass reading. You should check and realign your heading indicator regularly throughout your flight.
Every 15 minutes is a good rule of thumb. This will give you the most accurate directional readings and overall safety.
Be disciplined with these regular checks and you’ll avoid big deviations and stay on track.
It’s a small task but consistent alignments will improve navigation accuracy. Remember by doing these alignment and calibration you’ll be assured of your instrument’s reliability and have more confidence and peace of mind flying.
Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
A reliable heading indicator is key to safe and accurate navigation. Regular inspections and calibrations will ensure it’s working at its best and not surprise you during flight.
By doing these checks as part of your routine you’re being proactive and avoiding accuracy issues.
Frequent inspections will let you catch any signs of wear or malfunction early. This proactive approach will address problems before they get out of hand and reduce navigation risk.
With each check you’ll gain confidence in your instruments and be able to fly with ease and comfort. Calibration checks are just as important to ensure your heading indicator is aligned with the magnetic compass.
Consistent calibration will correct for any drift that can occur over time and keep your navigation as precise as possible. Knowing the importance of these adjustments will allow you to stay on course on every flight.
By sticking to a maintenance schedule you’re investing in your aircraft and your flight. It’s not just for your gear but for everyone on board and your own peace of mind.
By doing this you’re creating a culture of awareness and aviation excellence.

Best Practices for Accurate Navigation
Use the heading indicator with other important instruments like GPS and magnetic compass. During straight and level flight, both the magnetic compass and heading indicator provide accurate heading data. This way all instruments work together and you have a complete picture of your track.
Using multiple navigation tools makes it more accurate and safe for any flight. Regular checks and resetting of heading indicator is a must to maintain its accuracy. By resetting this instrument regularly you minimize the chances of errors in your navigation.
This makes flying safer and you can rely on your instruments. Though modern instruments are reliable, it’s always good to have alternative ways to determine your aircraft’s heading.
These backup plans are safety nets in case of instrument failure. This proactive approach ensures continuity in navigation so you don’t get stuck in the middle of your journey.
By following these best practices pilots prioritize safety and accuracy in every flight.
This methodical attention to detail not only enhances the overall flying experience but also fosters confidence and peace of mind for everyone involved.
Limitations and Considerations
Navigating the skies can be challenging, especially when considering the limitations of older heading indicators.
These instruments can become harder to read over time due to wear and tear, insufficient maintenance, or simply because they’re based on outdated designs.
Flying in the wrong direction could be disastrous, especially if pilots are unaware of their heading due to errors with the instrument.
This can present challenges for pilots, necessitating extra vigilance to ensure accurate readings. While heading indicators offer distinct benefits, a key advantage is their resilience to common issues that affect magnetic compasses.
Unlike compasses, heading indicators are not affected by banking, turbulence, or errors such as dip, making them more reliable under certain flight conditions.
This consistency is crucial when maintaining a steady course, especially in turbulent weather.
Heading indicators are particularly vital for instrument flying, where pilots rely heavily on their cockpit instruments to navigate.
The precision they provide greatly enhances a pilot’s situational awareness, allowing for safer and more confident flying, even in poor visibility conditions.
This reliability is indispensable in critical flight situations. Incorporating heading indicators into flight operations remains a best practice for pilots who seek to improve accuracy and awareness.
Despite their limitations, their unique advantages make them an essential tool in modern navigation, supporting pilots in achieving safe and efficient flights.
Investing in regular maintenance and updates ensures these instruments remain reliable, supporting every flight with cutting-edge capabilities.
Conclusion
The heading indicator is your best friend in the cockpit. It helps you stay on course so you fly safely and with confidence. Know and fix the errors in the heading indicator.
When you know these errors you will be able to navigate better and reduce the risk of in-flight accidents or collisions.
Best practices in using heading indicators can make a big difference in safety. Regular checks and maintenance of these instruments is key to keep them working right.
Ultimately, with consistent care and attention, heading indicators support pilots in achieving smooth and efficient flights, ensuring everyone onboard enjoys a safe journey.

